Verification of the sterilization effect of atmospheric pressure plasma on bacteria attached to smartphones.
We conducted an experiment aimed at visualizing the extent of the sterilization effect of atmospheric pressure plasma irradiation and clarifying its effectiveness and challenges!
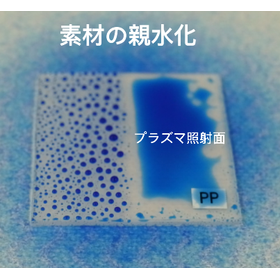
We examined the sterilization effect of atmospheric pressure plasma on microorganisms attached to the glass surface of smartphones and will introduce the details of the microorganisms involved and the results. Microorganisms were collected from the "untreated area" and the "area irradiated with atmospheric pressure plasma" on the glass surfaces of two staff members' smartphones using cotton swabs, and cultured. We then evaluated the sterilization effect by comparing the colonies of microorganisms formed on the Petri dishes from both areas. As a result, mainly "bacteria from hands" and "bacteria from the environment" were identified, with at least three types of microorganisms observed. On the plates after plasma irradiation, the number of bacterial or yeast colonies decreased compared to the "untreated" ones. Fungi and actinobacteria were still observed after plasma irradiation. [Observed Microorganisms] ■ Bacteria or Yeast ■ Filamentous Fungi (Mold) ■ Actinobacteria *For more details, please refer to the related links or feel free to contact us.
basic information
**Conclusion** ■ Atmospheric pressure plasma treatment is expected to reduce microorganisms such as "bacteria and yeast from fingers" that adhere to smartphones. ■ On the other hand, there are highly resistant microorganisms like mold spores, suggesting that optimizing irradiation conditions may be necessary to achieve complete sterilization. *For more details, please refer to the related links or feel free to contact us.*
Price range
Delivery Time
Applications/Examples of results
For more details, please refer to the related links or feel free to contact us.
catalog(1)
Download All CatalogsRecommended products
Distributors
Aqua Corporation is a company that focuses on the production of various devices, including equipment for cleaning glass substrates. The devices are primarily custom-made rather than off-the-shelf products, and we manufacture products that meet our customers' needs. We also engage in various resin processing businesses. We have developed our own user-friendly and highly efficient atmospheric pressure plasma equipment and propose and sell applications for new technologies. We provide technical consulting for vacuum equipment, support for maintaining the quality of vacuum film formation, and ensuring stable operation of vacuum devices. For various cleaning devices, resin processing, and atmospheric pressure plasma surface modification equipment, please leave it to us.