[ED] Electron Diffraction Method
ED is a method for investigating crystal structures from diffraction patterns obtained by irradiating a sample with an electron beam.
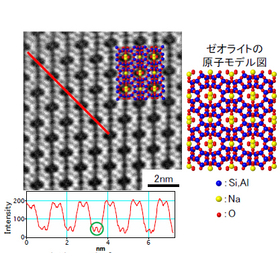
ED is a method for investigating crystal structures from diffraction patterns obtained by irradiating a sample with an electron beam. - Crystallographic information about the material can be obtained. In the case of a transmission electron microscope, a single crystal shows regularly arranged diffraction spots, a polycrystal shows concentric circular rings, and an amorphous material shows broad circular electron diffraction patterns. - It is possible to examine the crystal structure of small regions observed with a transmission electron microscope. - By combining the crystal structure with elemental analysis results from the EDX method, it is also possible to identify materials that possess crystallinity.
basic information
When the incident electrons meet the Bragg condition at an angle with respect to the crystal lattice planes, they undergo elastic scattering. The scattered electrons interfere with each other, but only those electrons that satisfy the Bragg condition have intensity as diffracted waves in specific directions, forming diffraction spots. By analyzing the positional relationship between the transmitted light and the multiple diffraction spots, information about the crystal structure of the sample can be obtained.
Price information
-
Delivery Time
Applications/Examples of results
Evaluation of crystallinity, identification of crystal structure, evaluation of crystal orientation, evaluation of crystal alignment for materials such as Si, compound semiconductors, oxide semiconductors, and metals.
Detailed information
-

Please consult with us first. ★ We will start with a proposal for an analysis plan ★ We can, of course, meet at your company for discussions. We will carefully explain the analysis results and leave no questions unanswered. Please contact us at 03-3749-2525 or info@mst.or.jp!
-

We will hold a visiting seminar. ★We offer free seminars with engineers tailored to our customers' needs★ We will introduce analytical techniques and explain analytical data according to your requests. ◆Examples of seminar content - A broad explanation of MST analysis methods - A detailed explanation of specific analysis methods from the principles - An explanation of the analytical data requested by the customer Please contact us at 03-3749-2525 or info@mst.or.jp!
Recommended products
Distributors
MST is a foundation that provides contract analysis services. We possess various analytical instruments such as TEM, SIMS, and XRD to meet your analysis needs. Our knowledgeable sales representatives will propose appropriate analysis plans. We are also available for consultations at your company, of course. We have obtained ISO 9001 and ISO 27001 certifications. Please feel free to consult us for product development, identifying causes of defects, and patent investigations! MST will guide you to solutions for your "troubles"!