(S)TEM (Scanning Transmission Electron Microscopy)
Elemental analysis, state evaluation, particle size analysis, and acquisition of three-dimensional structural images at the nanoscale.
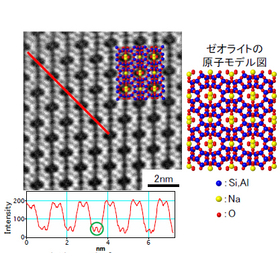
TEM (Transmission Electron Microscopy) is a method that involves irradiating a thin sample with an electron beam, imaging the electrons that have passed through or scattered from the sample, and observing it at high magnification. ■ Advantages - Enlarged images can be obtained with sub-nanometer spatial resolution, allowing for the observation and analysis of the sample's fine structure and lattice defects. - It is possible to evaluate the crystallinity of the sample and identify materials. - By fabricating samples using FIB (Focused Ion Beam), it is possible to observe specific locations within a device with pinpoint accuracy. - By combining optional features, it is also possible to analyze the composition and state of localized areas. ■ Disadvantages - It is necessary to thin the sample (in some cases, thinning may be difficult for certain samples). - It does not observe individual atoms but rather displays average information in the thickness direction of the sample (typically about 0.1 μm thick). - Sample processing and observation may lead to alteration or deformation of the sample.
basic information
When electrons pass through a thin sample, some electrons continue straight through the sample, while others are scattered due to the type of atoms and crystallinity. The scattered electrons can be broadly classified into elastic scattered electrons and inelastic scattered electrons, and by selecting and imaging these electrons according to the purpose, insights into the morphology, crystal structure, composition, and electronic states within the sample can be obtained.
Price information
-
Delivery Time
Applications/Examples of results
- Observation of various shapes and forms, three-dimensional shape evaluation of fine particles - Evaluation of various dimensions (laminated film thickness, dimensions such as gate length, etc.) - Observation of crystal defects (dislocations, stacking faults, grain boundaries, precipitates, etc.) - Evaluation of crystallinity (orientation, degree of crystallization, grain size, etc.) - Failure analysis of specific locations (investigation of the causes of defects) - Evaluation of foreign substances (morphological observation, qualitative analysis using EDX, etc.) - Evaluation of stress and strain and so on.
Detailed information
-

First, please consult with us. ★ We will start with a proposal for an analysis plan ★ Meetings at your company are, of course, possible. We will carefully explain the analysis results and leave no questions unanswered. Please contact us at 03-3749-2525 or info@mst.or.jp!
-

We will hold a visiting seminar. ★ We offer free seminars with engineers tailored to your needs ★ We will introduce analytical techniques and explain analytical data according to your requests. ◆ Example seminar content - A broad explanation of MST analytical methods - A detailed explanation of specific analytical methods from the principles - An explanation of the analytical data requested by the customer Please contact us at 03-3749-2525 or info@mst.or.jp!
News about this product(2)
-

Notice of the Electron Microscope and FIB Seminar hosted by Hitachi High-Technologies Corporation
The seminar "Hitachi Materials Analysis Seminar 2012 (Nagoya)" hosted by Hitachi High-Technologies Corporation will feature a lecturer from the MST (Foundation for the Promotion of Material Science and Technology). The analysis of lithium-ion secondary batteries will be reviewed based on analytical data. We look forward to your participation. ● Date and Venue February 3, 2012 (Friday) 13:00 - 17:40 17th Floor, Takisada Building, Nagoya City, Aichi Prefecture ● Participation Fee and Registration For more details, please visit the Hitachi High-Technologies website. ● Overview of the MST Lecturer's Course - Title Cryo FIB-TEM Method under Controlled Atmosphere - Application to Lithium-Ion Secondary Batteries - Lecturer TMG Eguchi, Analysis and Evaluation Department, Foundation for the Promotion of Material Science and Technology
-

[MST Homepage] Analysis Case "Heating Degradation Test of Lithium-Ion Secondary Batteries" Published
The MST website has published analysis case studies. ◆Title Heating Degradation Test of Lithium-Ion Secondary Batteries ~Samples after heating degradation can be evaluated using LC/MS/MS, TOF-SIMS, TEM+EDX, etc.~ ◆Measurement and Processing Methods TOF-SIMS, TEM, LC/MS/MS, FIB, μ-sampling, lift-out, disassembly, atmosphere control ◆Product Field Secondary Batteries ◆Analysis Objectives Composition evaluation, identification, chemical bonding state evaluation, film thickness evaluation, degradation investigation, reliability evaluation ◆Overview The development of lithium-ion secondary batteries faces challenges such as performance enhancement, longevity, and reliability improvement. To address these challenges, understanding the degradation mechanisms of the batteries is crucial. In this instance, a heating degradation test was conducted to evaluate the degradation mechanisms due to temperature. After the heating degradation test, samples that showed significant capacity reduction were evaluated using LC/MS/MS for the electrolyte, TOF-SIMS for the anode surface, and FIB-TEM+EDX for the anode cross-section. ★★For detailed data, please refer to the link★★
Recommended products
Distributors
MST is a foundation that provides contract analysis services. We possess various analytical instruments such as TEM, SIMS, and XRD to meet your analysis needs. Our knowledgeable sales representatives will propose appropriate analysis plans. We are also available for consultations at your company, of course. We have obtained ISO 9001 and ISO 27001 certifications. Please feel free to consult us for product development, identifying causes of defects, and patent investigations! MST will guide you to solutions for your "troubles"!